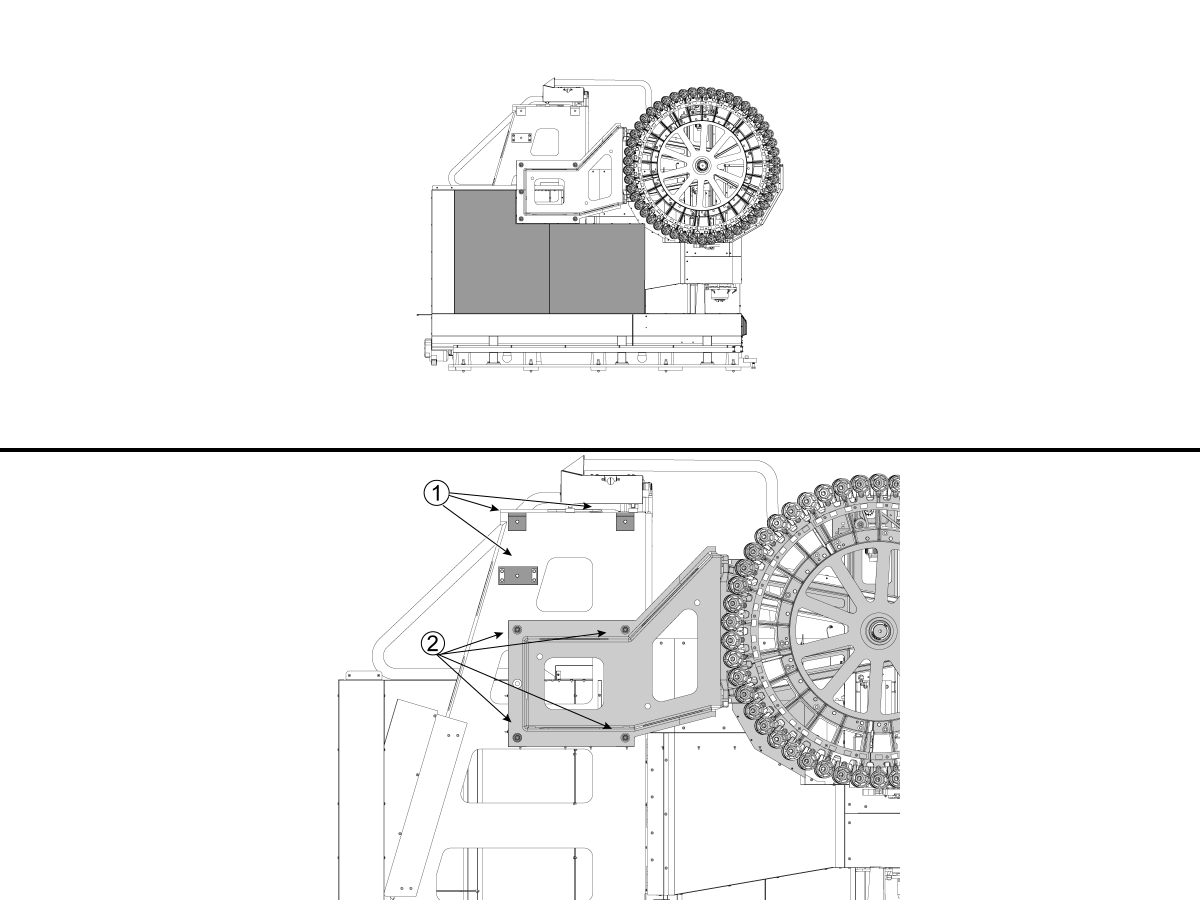
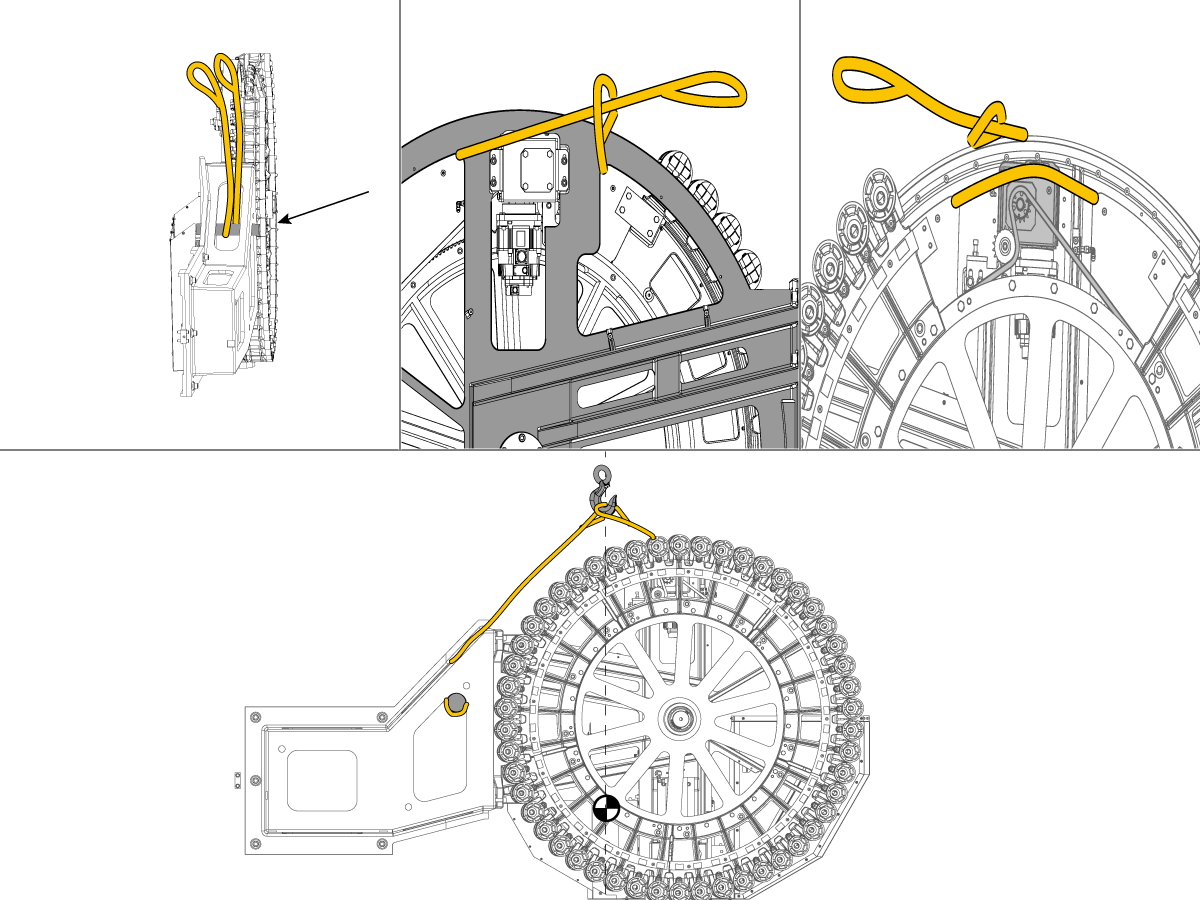
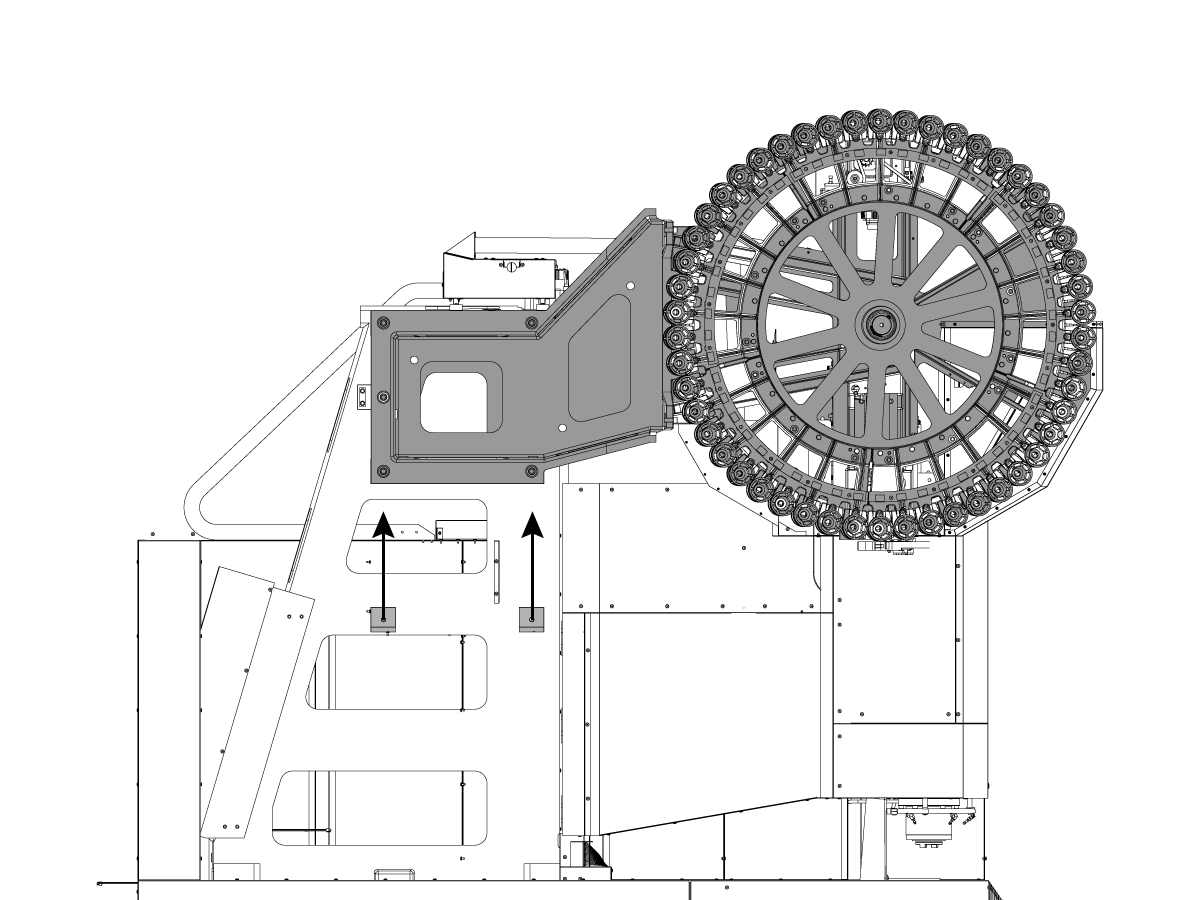
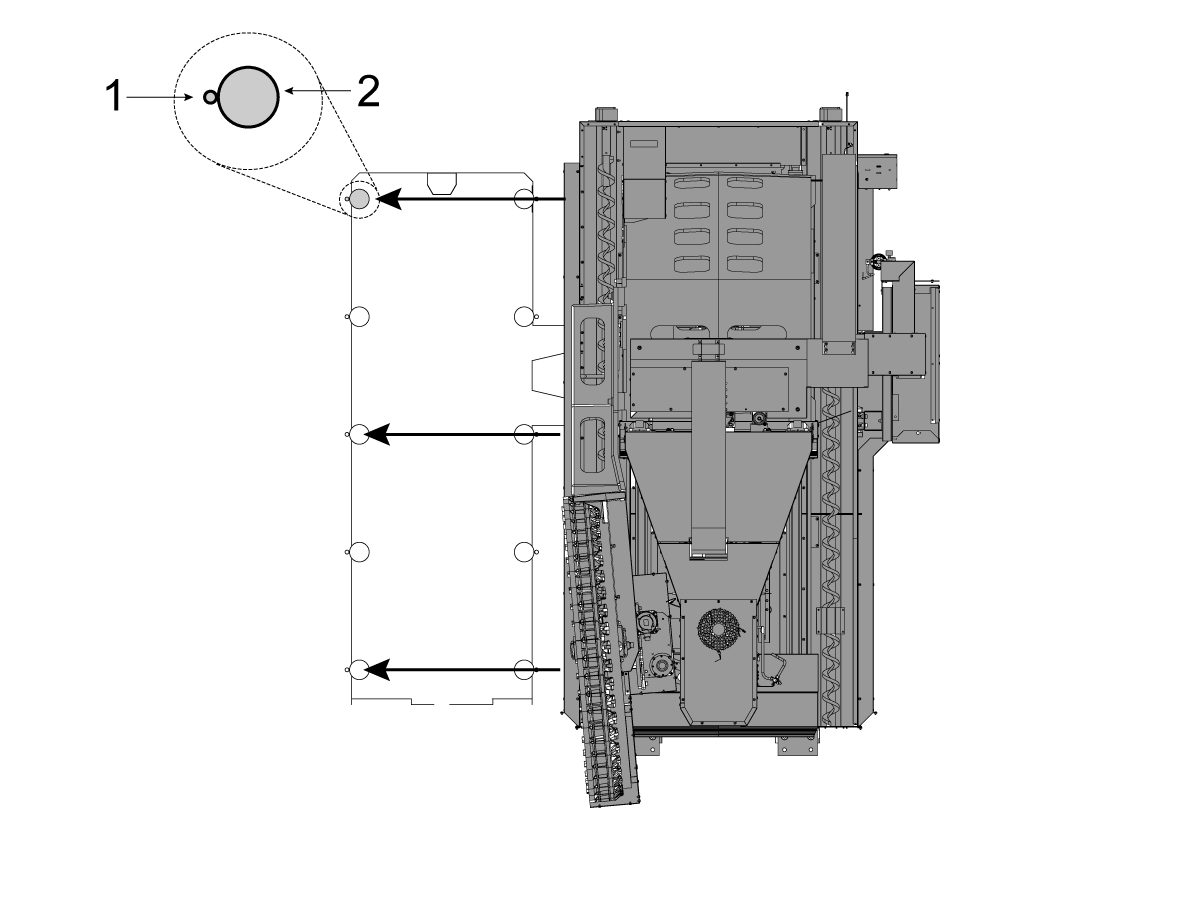
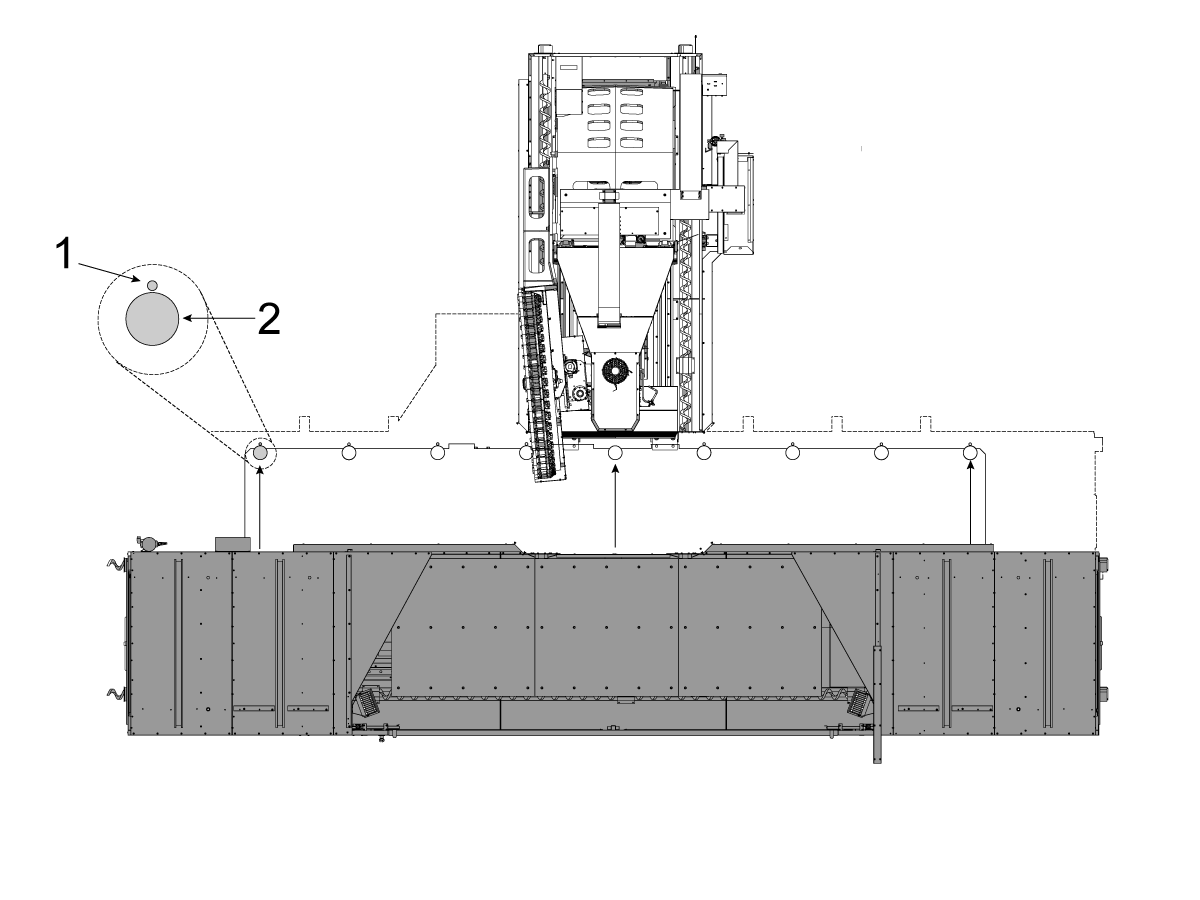
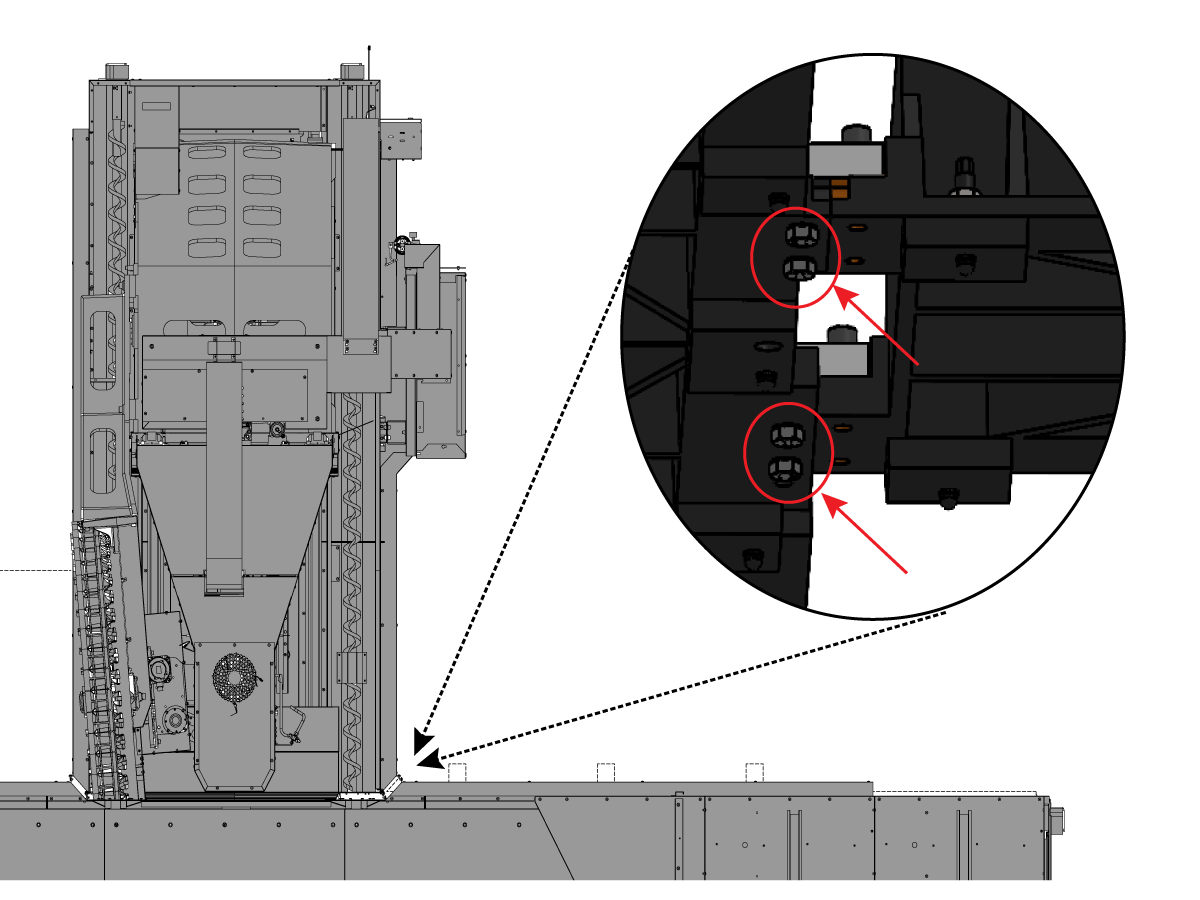
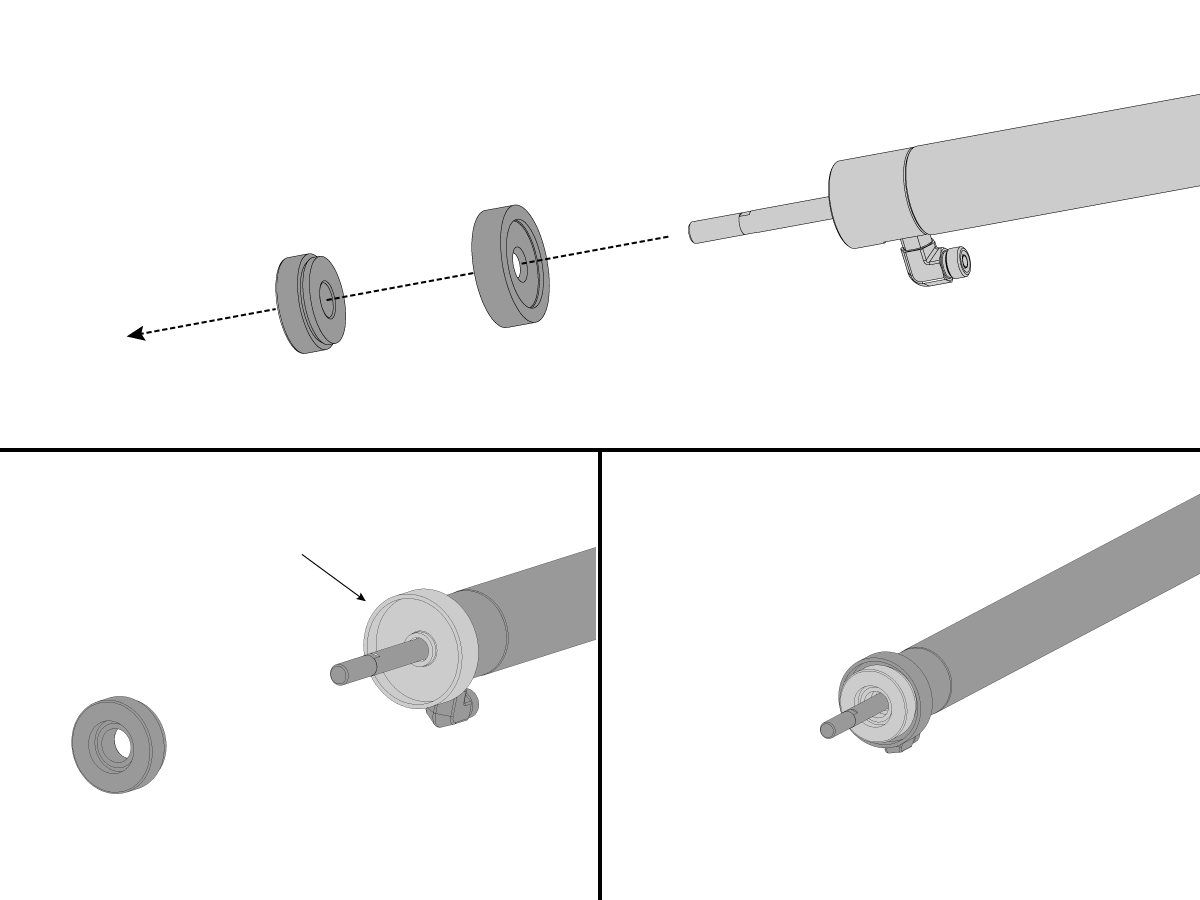
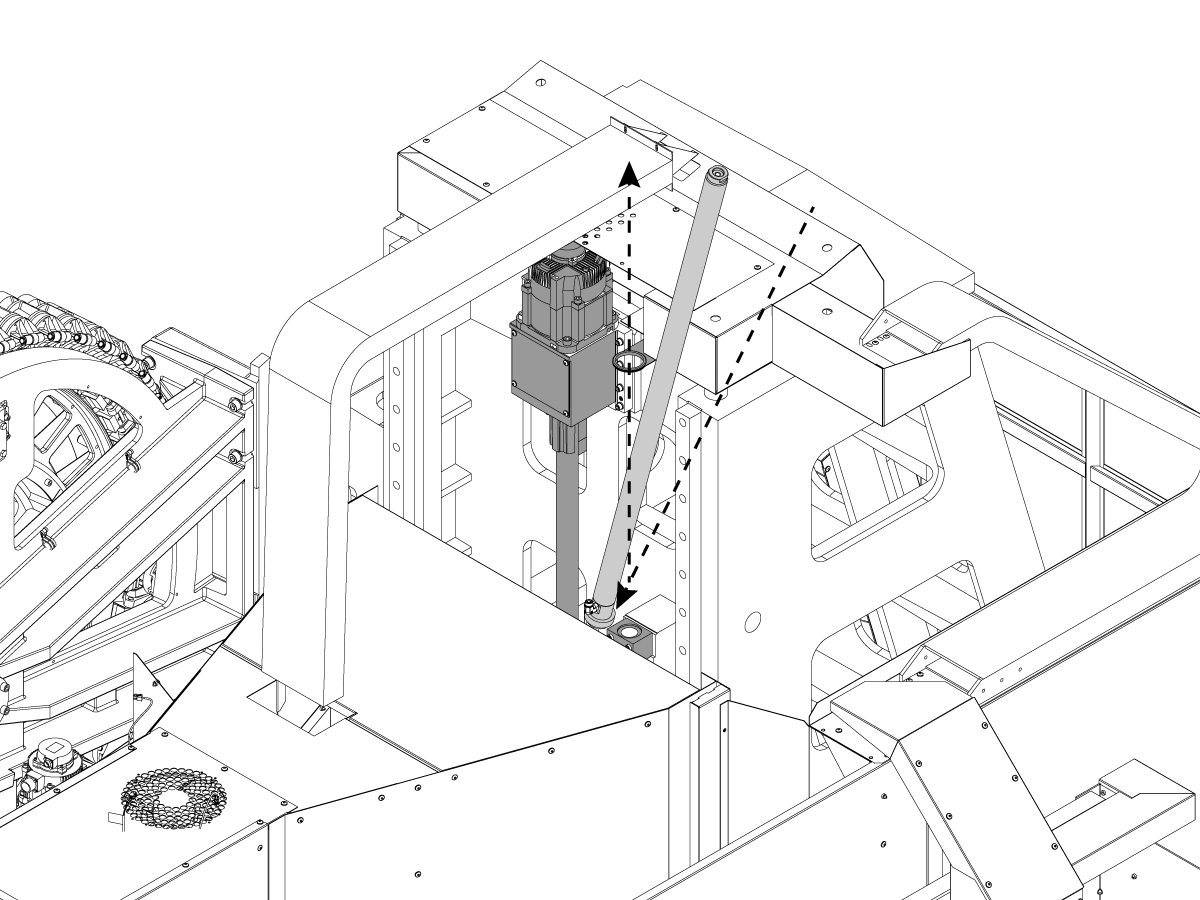
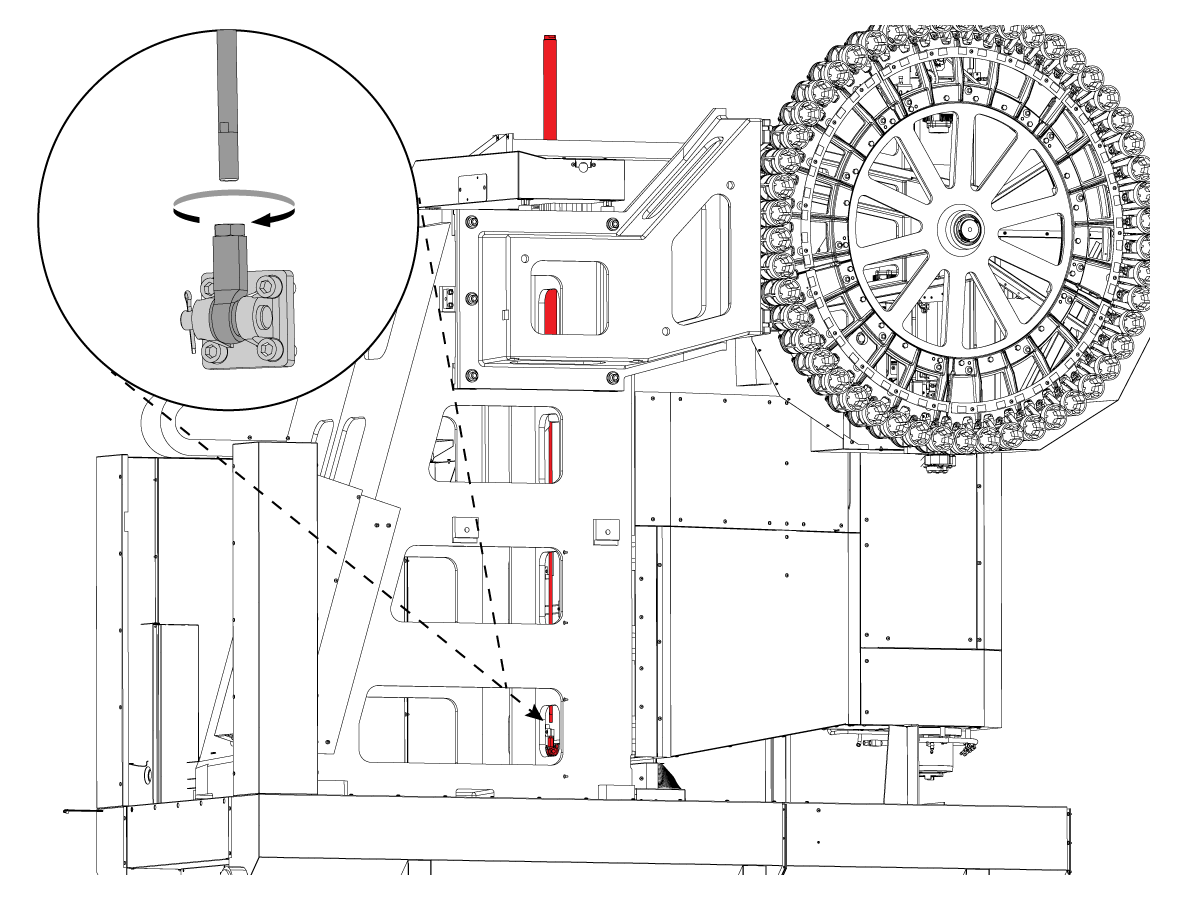
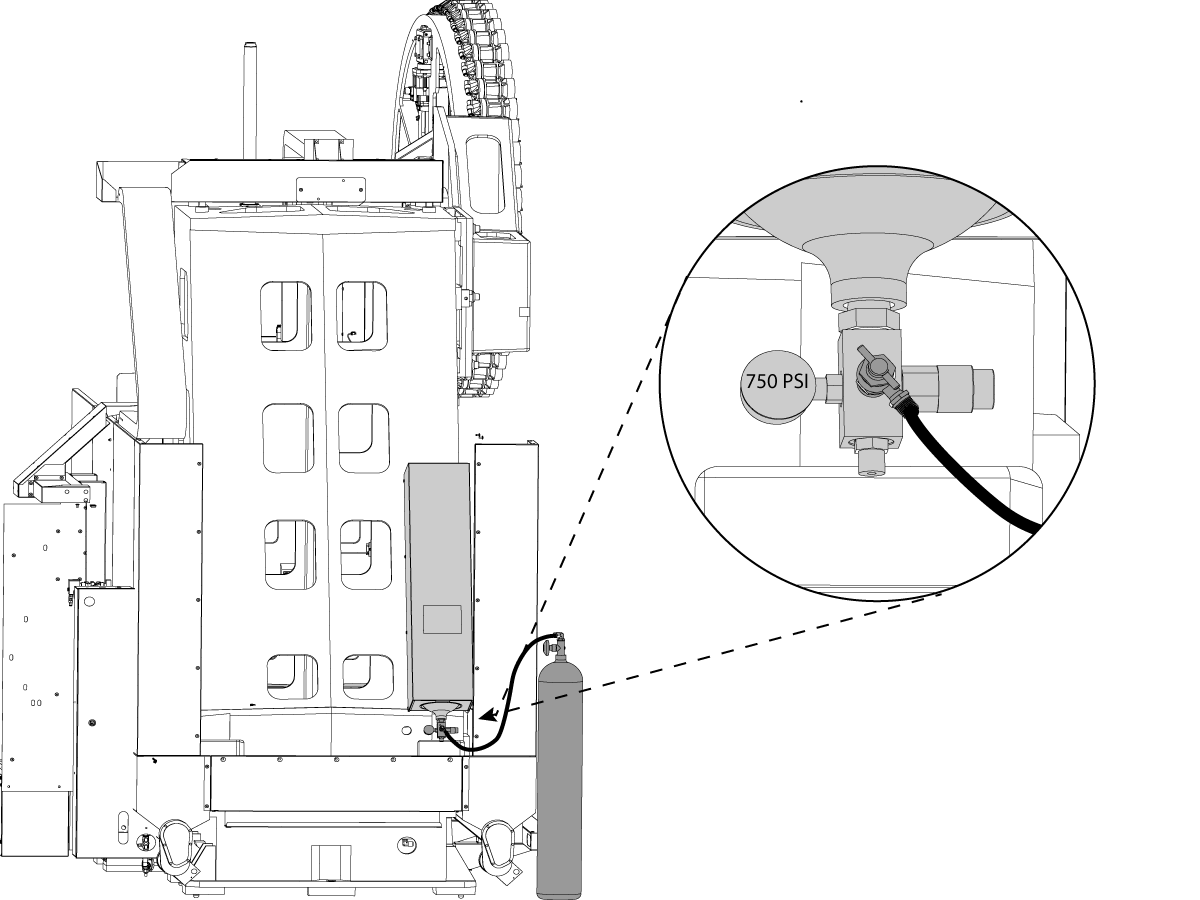
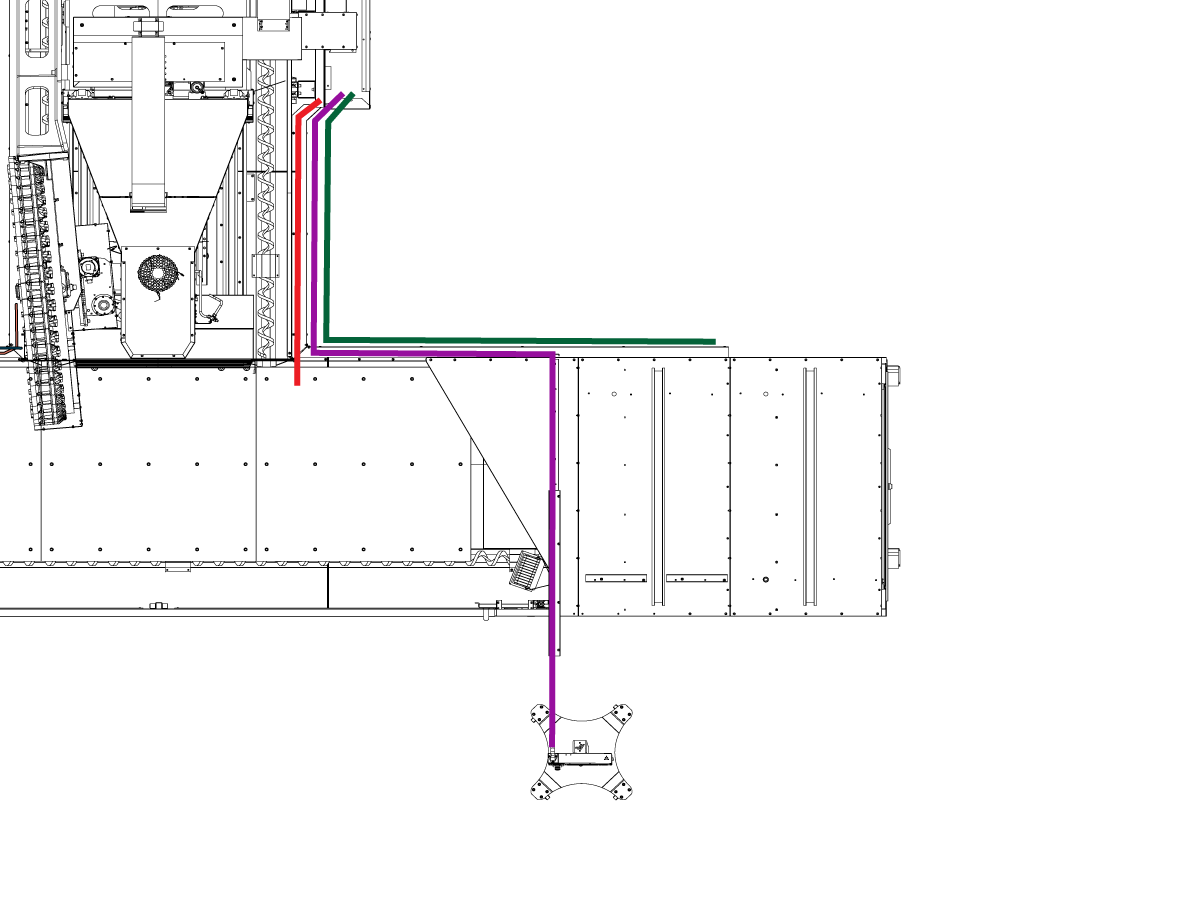
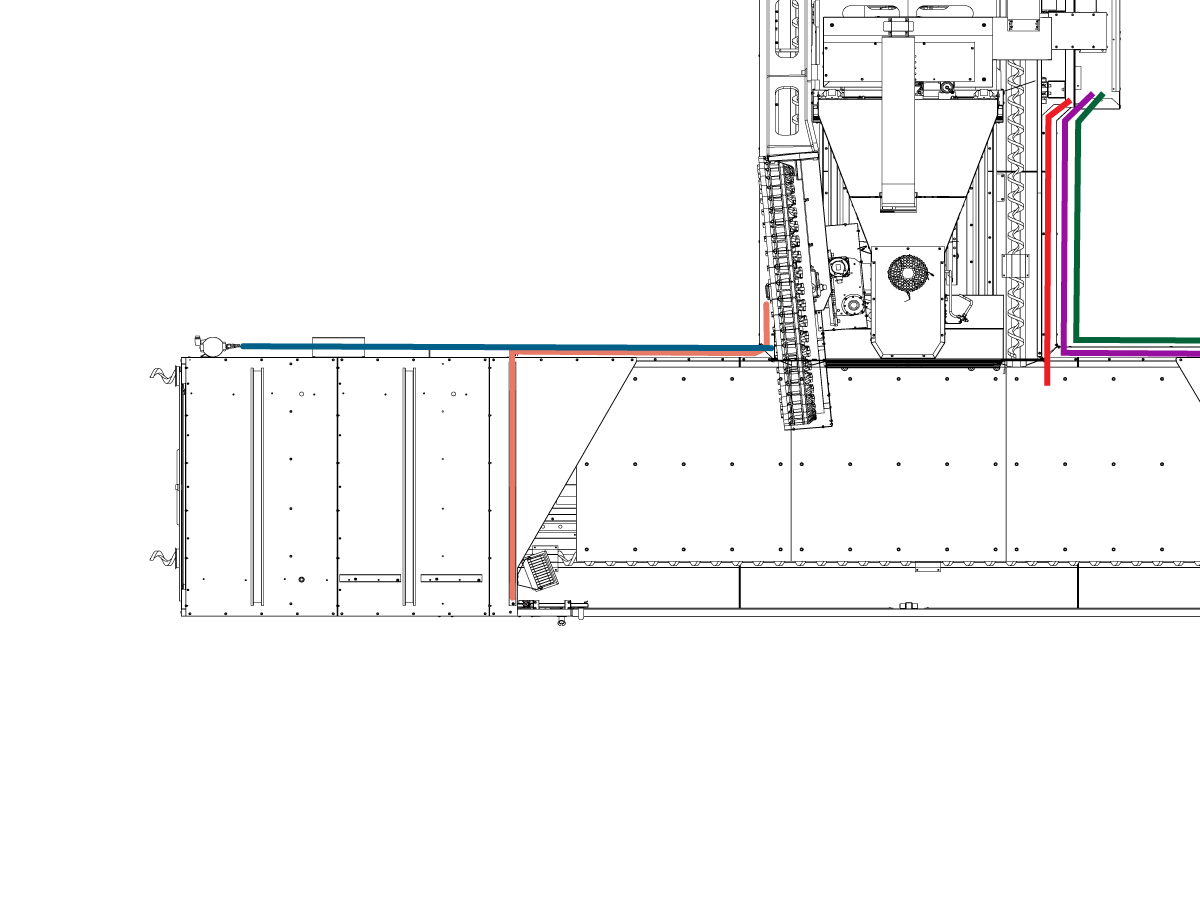
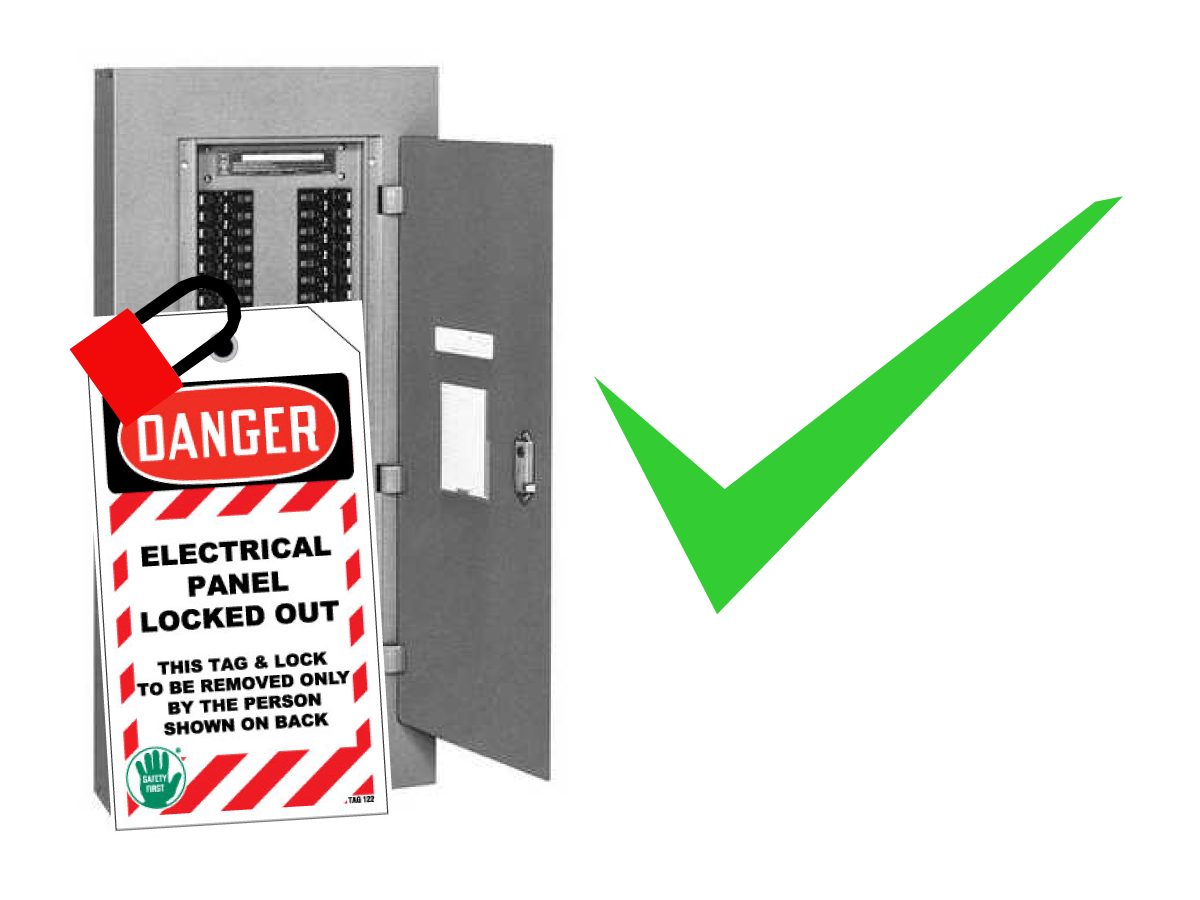
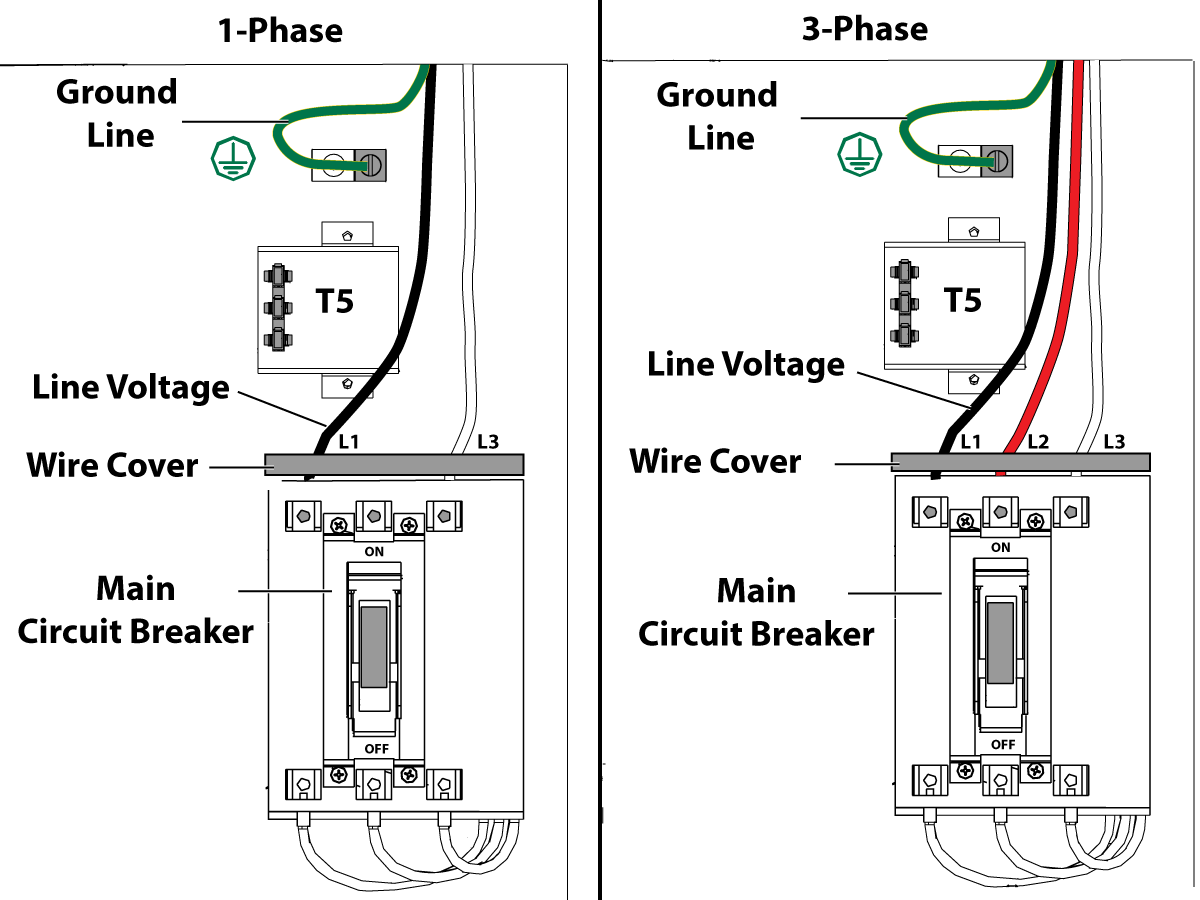
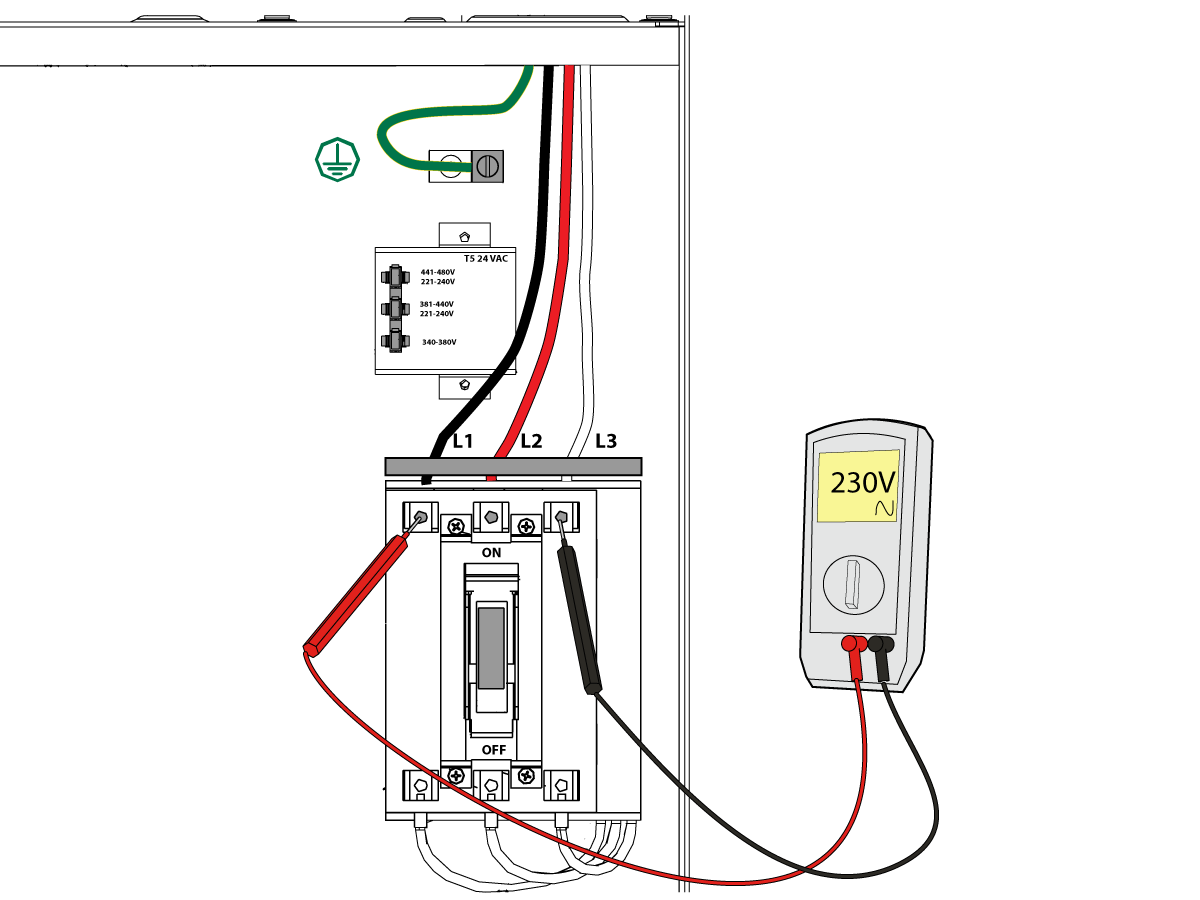
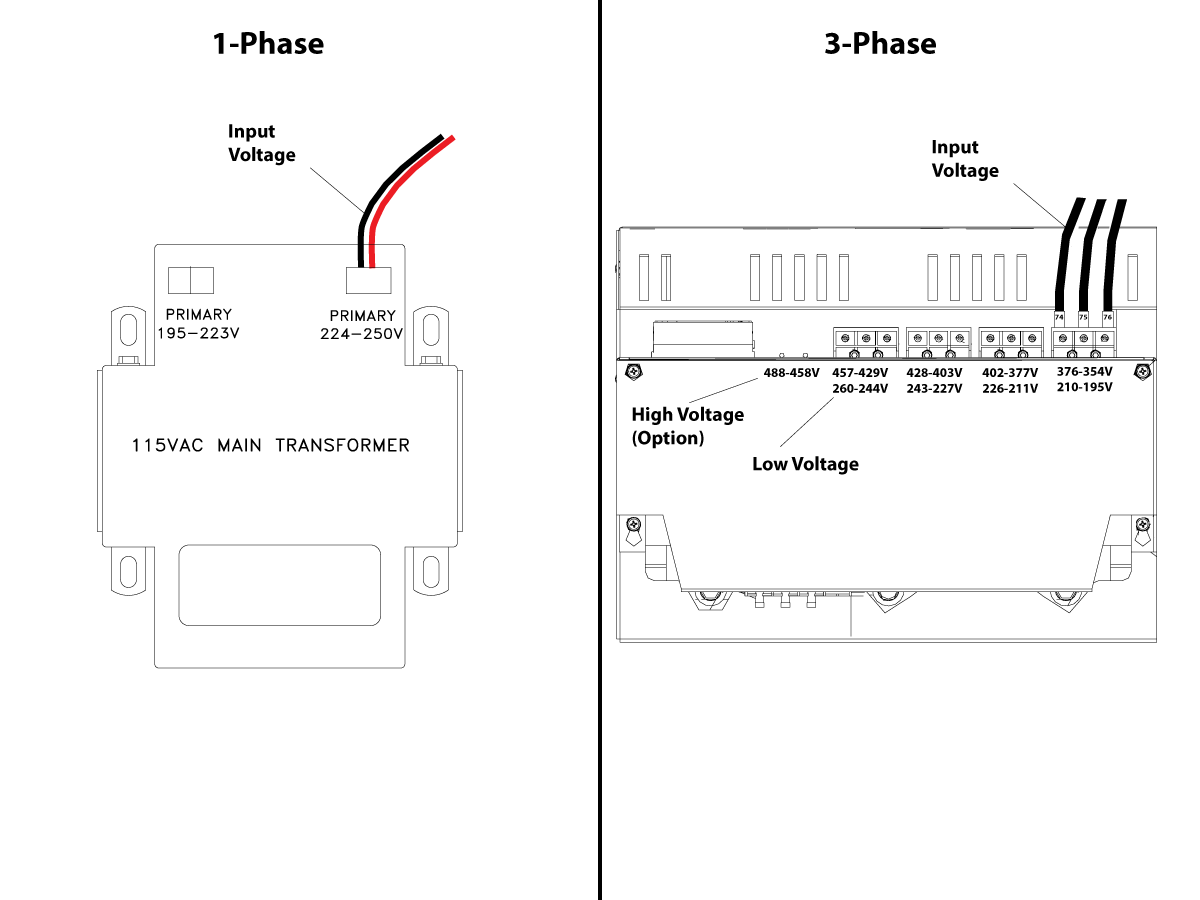
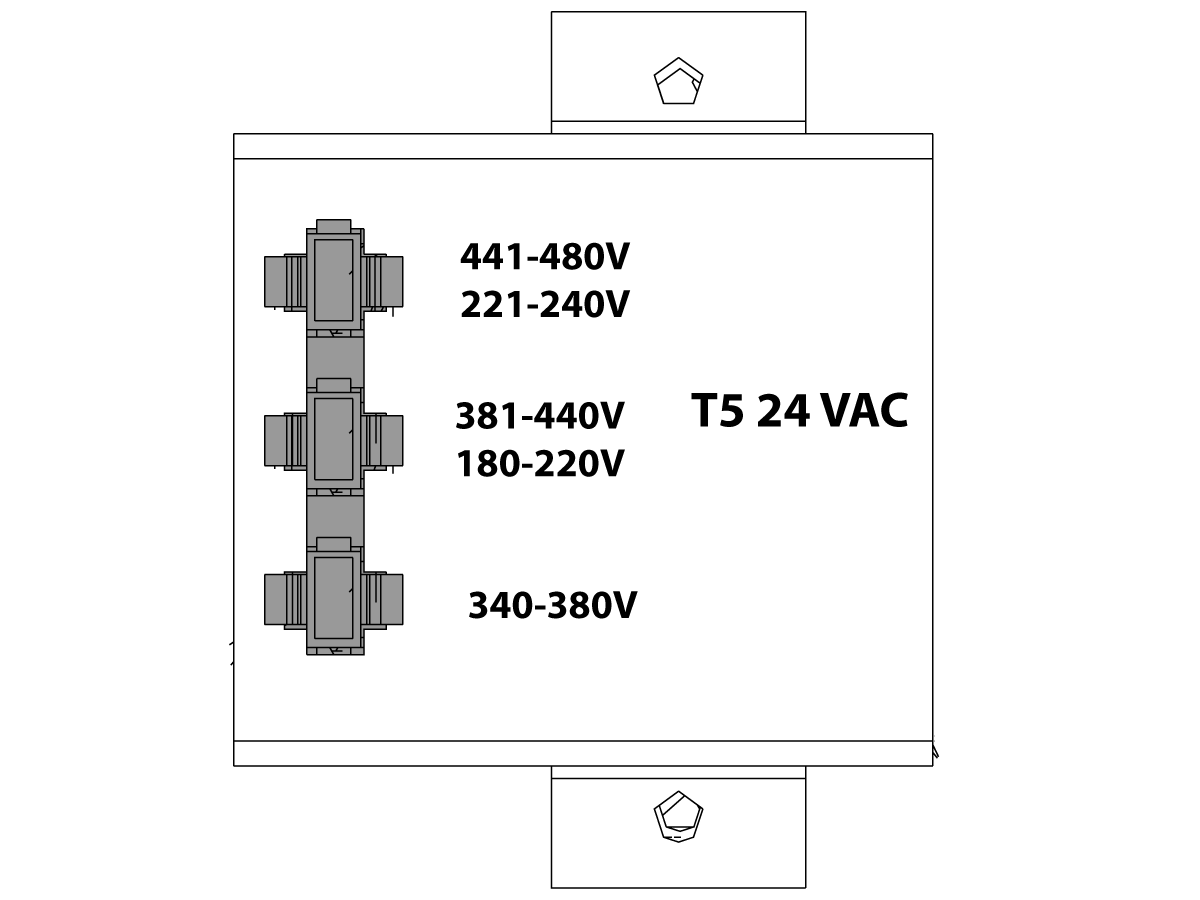
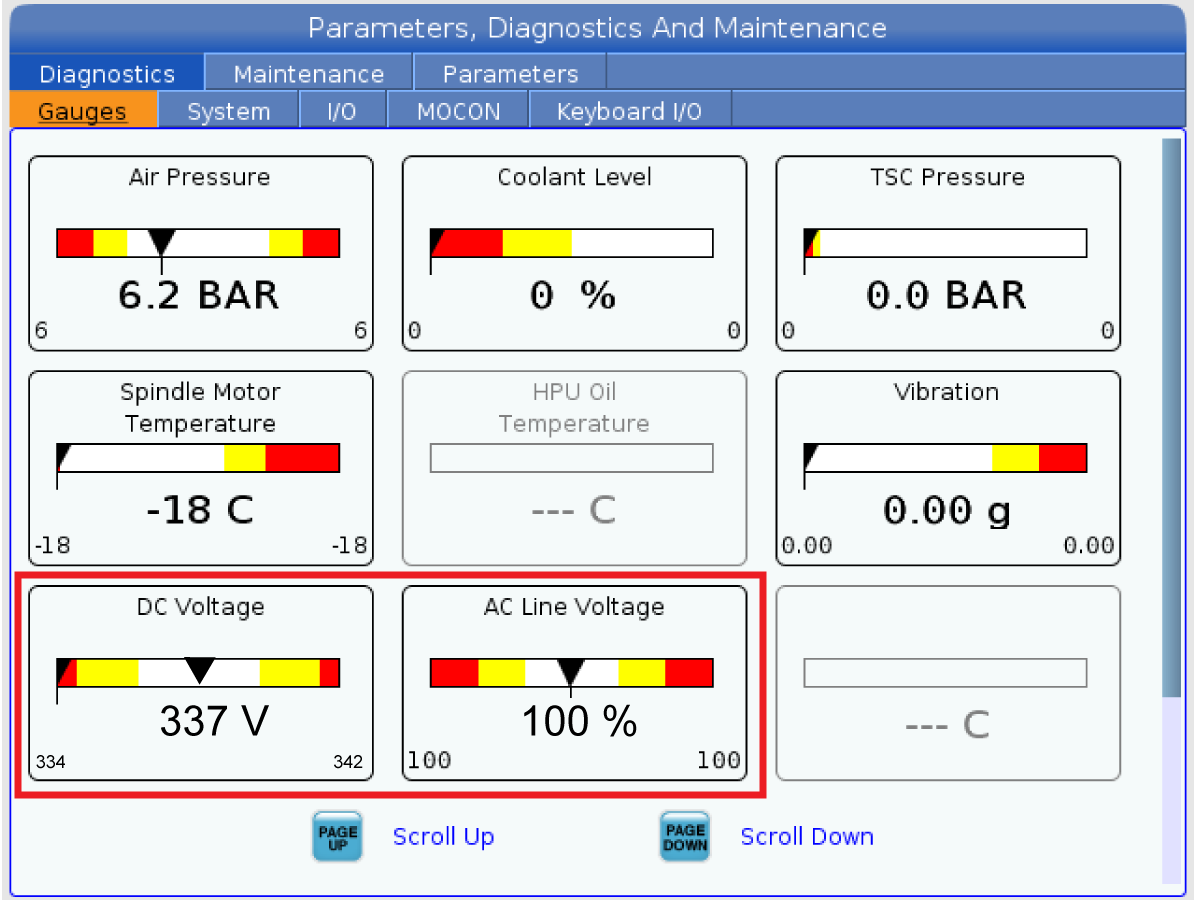
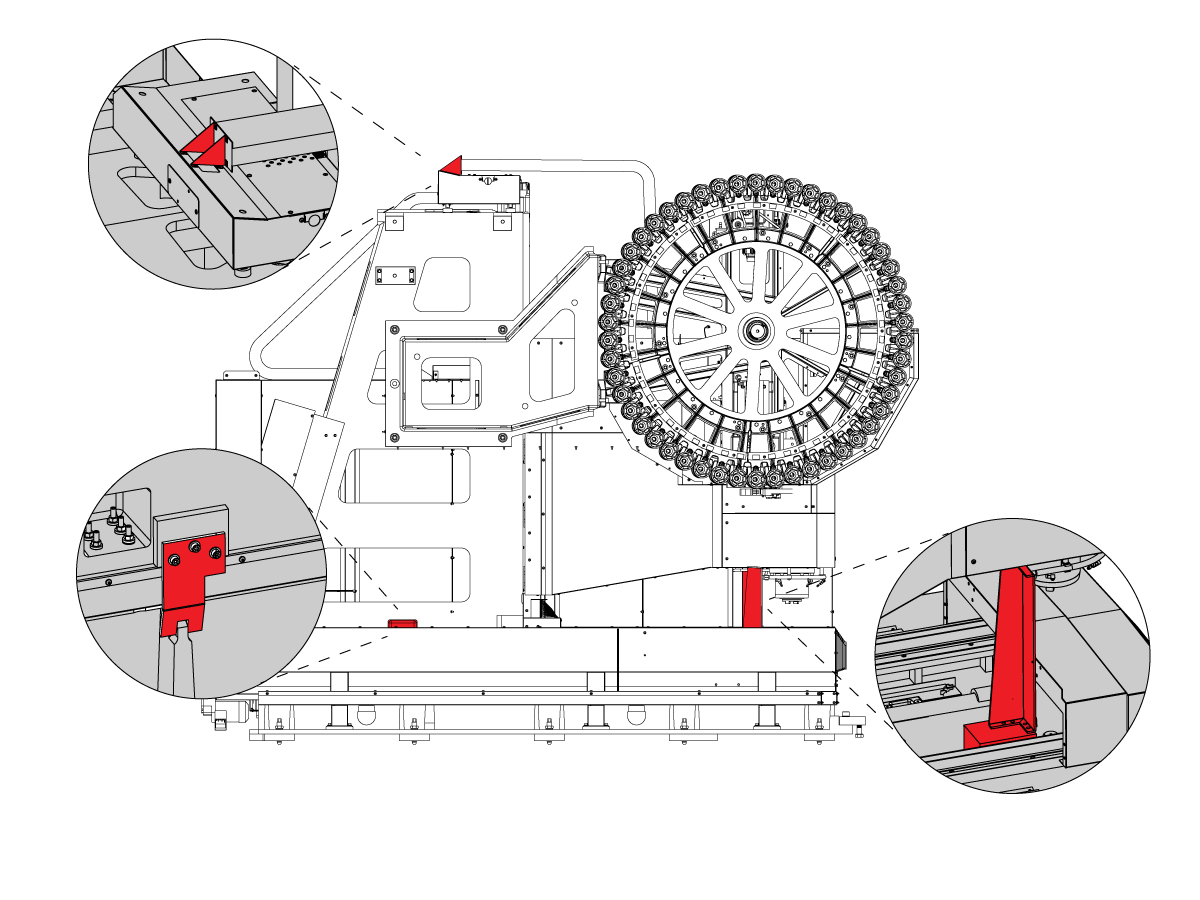
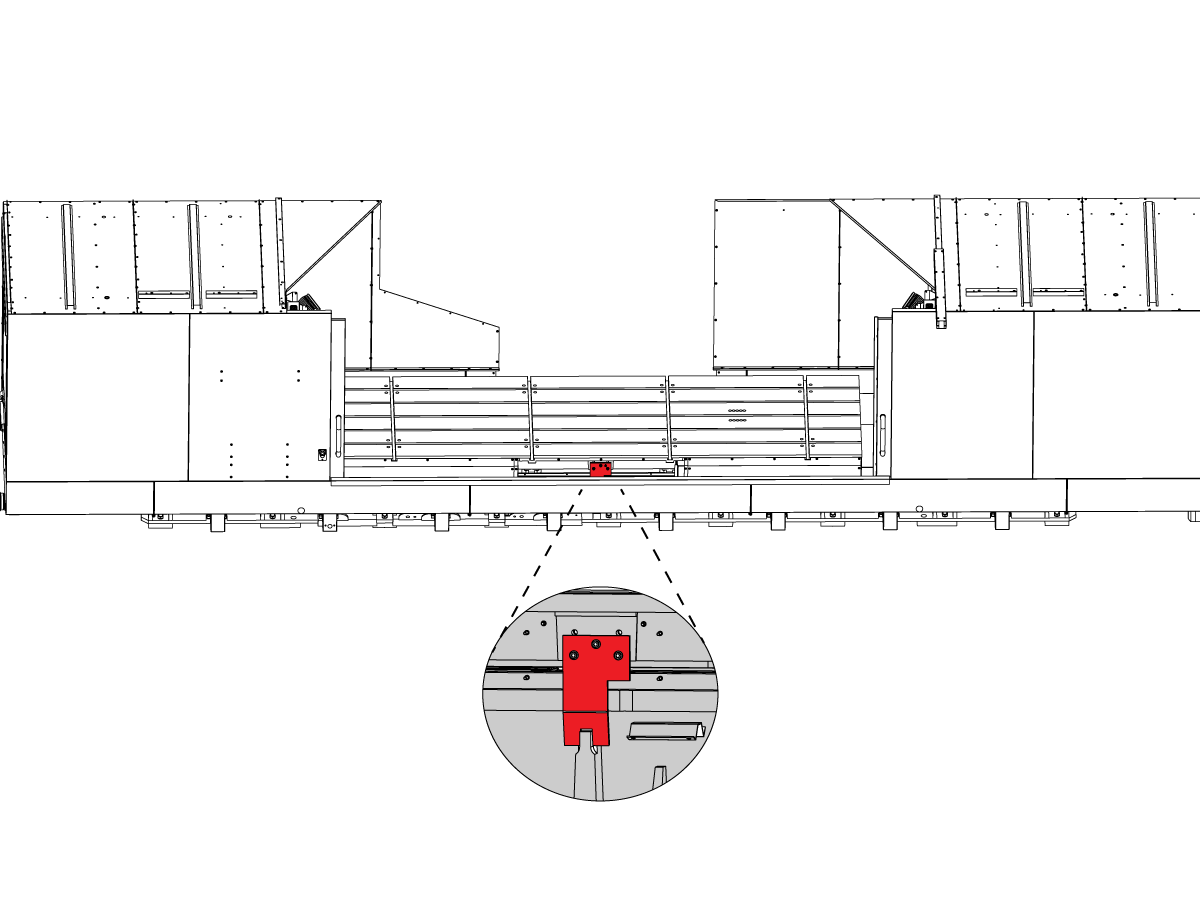
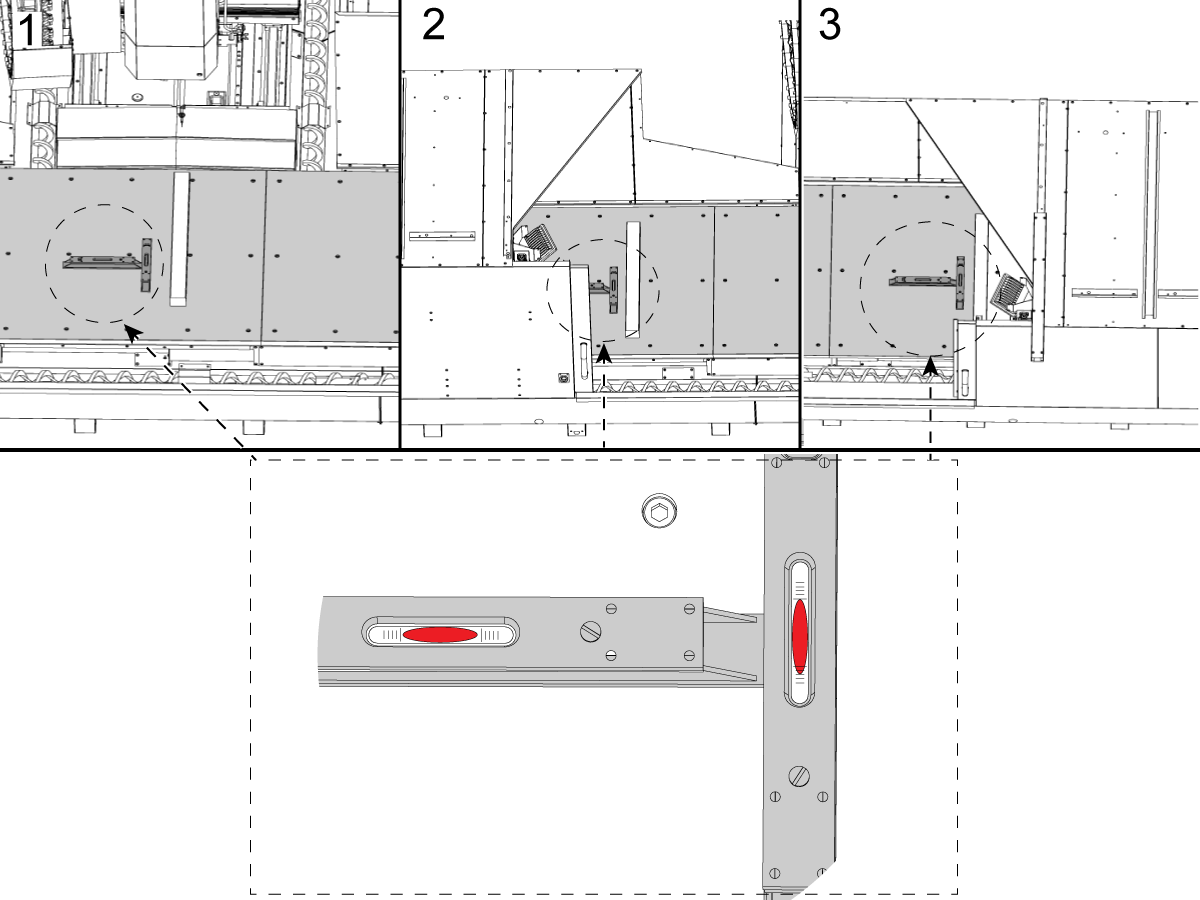
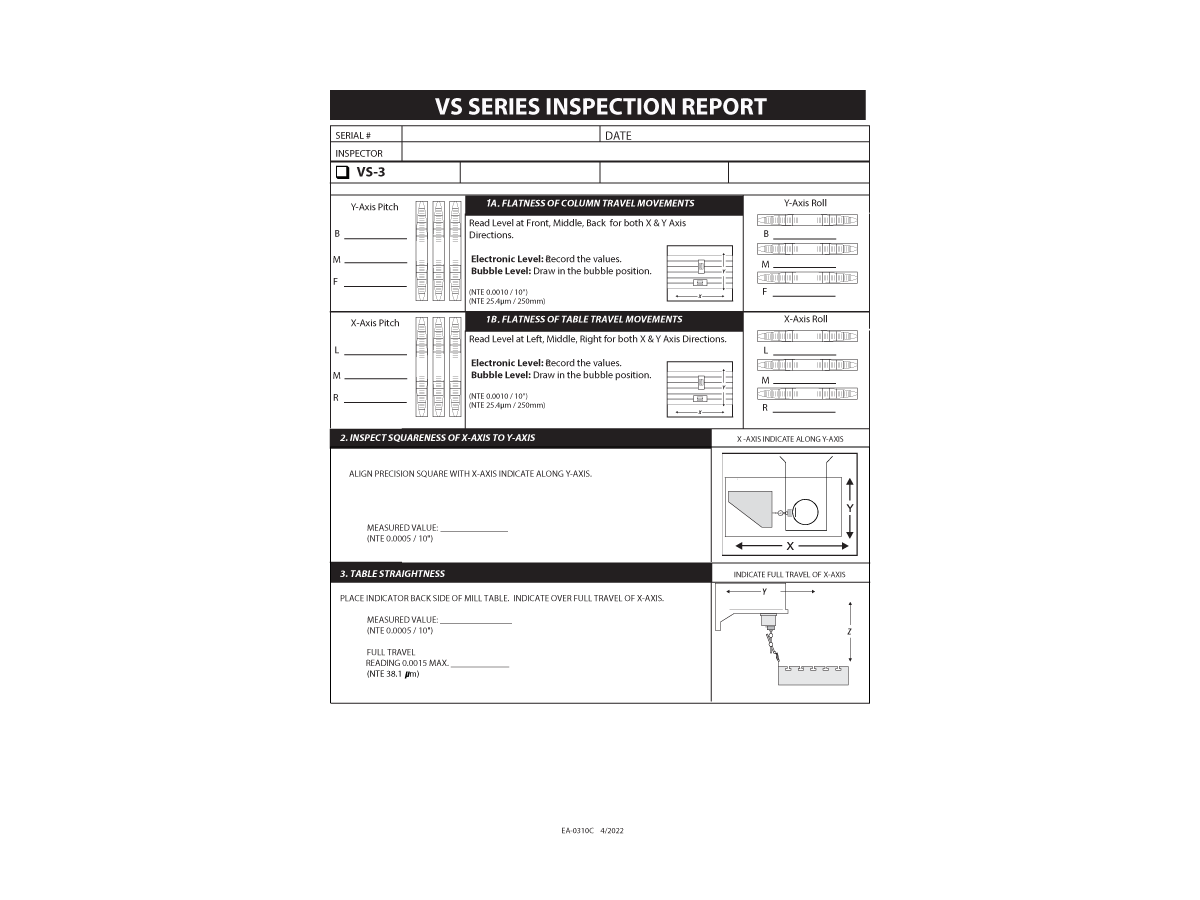
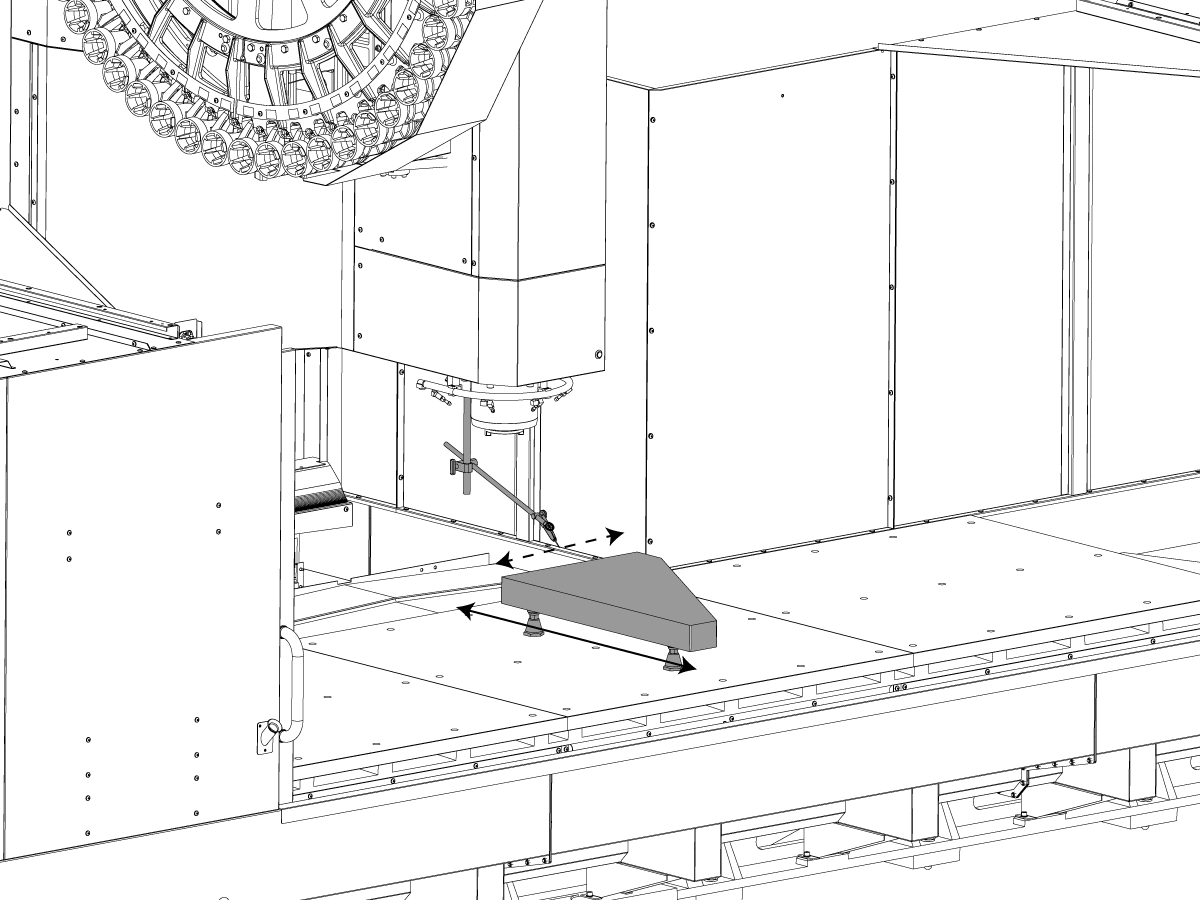
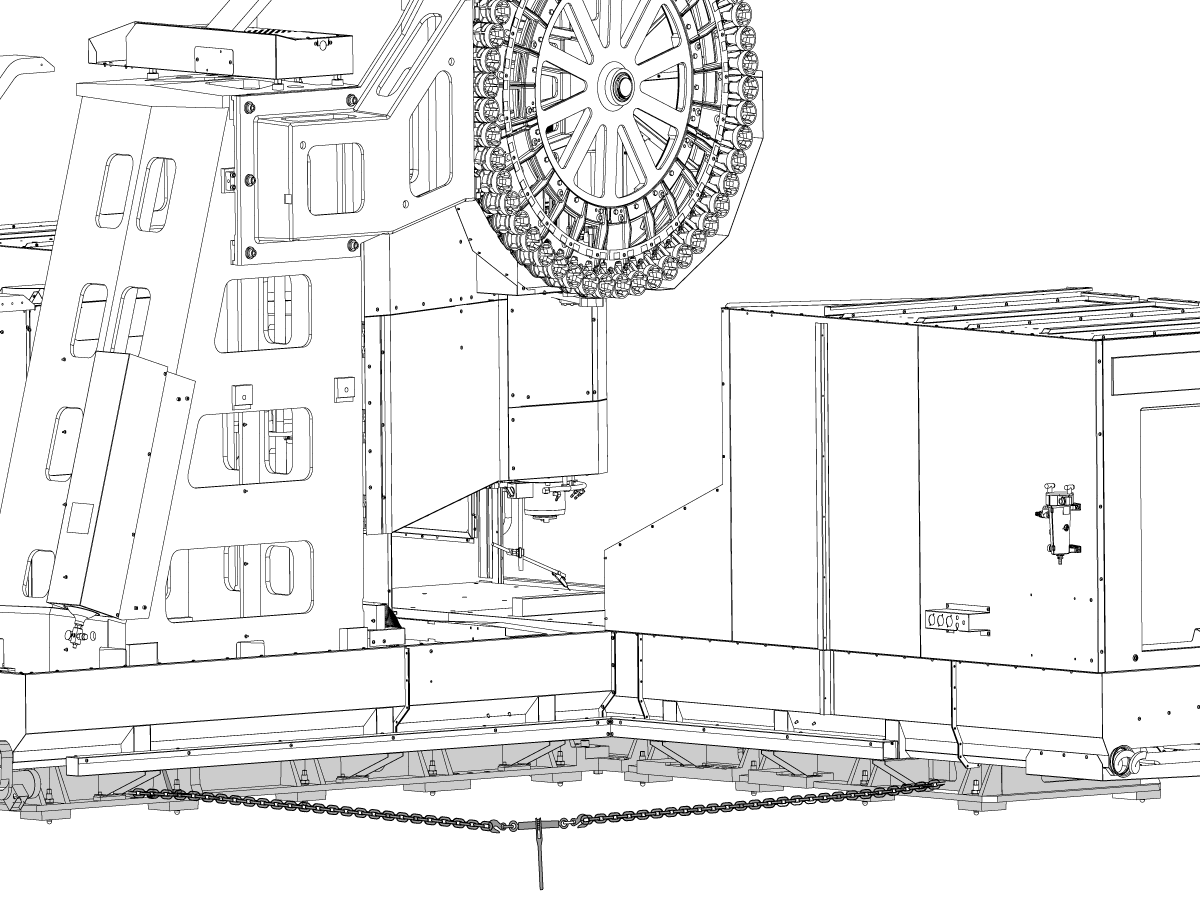
-
máquinas
Main Menu
-
Fresadoras verticales
Fresadoras verticalesFresadoras verticales View All
- Fresadoras verticales
- Serie VF
- Máquinas universales
- Series VR
- VP-5 prismático
- CMV con cambio de paletas
- Mini Mills
- Máquinas de moldeo
- Centros de taladrado de alta velocidad
- Serie de taladrado/roscado/fresado
- Fresadoras tipo Toolroom
- Fresadoras compactas
- Serie de puentes
- Router de láminas
- CMV de gran tamaño
- Fresadoras de doble columna
- Simulador del control
- Fresadora con cavidades
- Cargador automático de piezas para fresadora
- Cargador automático de piezas de carga lateral CMV/UMC
- Cargador de piezas automático compacto
-
Soluciones multieje
Soluciones multiejeSoluciones multieje View All
-
Tornos
TornosTornos View All
-
Fresadoras horizontales
Fresadoras horizontalesFresadoras horizontales View All
-
Cuartos ejes y divisores
Cuartos ejes y divisoresCuartos ejes y divisores View All
-
Sistemas de automatización
Sistemas de automatizaciónSistemas de automatización View All
-
Máquinas de sobremesa
Máquinas de sobremesaMáquinas de sobremesa View All
-
Equipo de taller
Equipo de tallerEquipo de taller View All
-
Máquinas de bolsillo
Máquinas de bolsilloMáquinas de bolsillo View All
ENLACES RÁPIDOS Special Series Special SeriesHERRAMIENTAS DE COMPRAS¿QUIERE HABLAR CON ALGUIEN?En su Haas Factory Outlet (HFO) pueden resolver sus dudas y orientarle sobre las mejores opciones.
CONTACT YOUR DISTRIBUTOR > -
Fresadoras verticales
-
Opciones
Main Menu
-
 Husillos
HusillosHusillos View All
Husillos
HusillosHusillos View All -
 Cambiadores de herramientas
Cambiadores de herramientasCambiadores de herramientas View All
Cambiadores de herramientas
Cambiadores de herramientasCambiadores de herramientas View All -
 4.º | 5.º eje
4.º | 5.º eje4.º | 5.º eje View All
4.º | 5.º eje
4.º | 5.º eje4.º | 5.º eje View All -
 Torretas y herramientas vivas
Torretas y herramientas vivasTorretas y herramientas vivas View All
Torretas y herramientas vivas
Torretas y herramientas vivasTorretas y herramientas vivas View All -
 Palpado
PalpadoPalpado View All
Palpado
PalpadoPalpado View All -
 Manejo del soluble refrigerante y virutas
Manejo del soluble refrigerante y virutasManejo del soluble refrigerante y virutas View All
Manejo del soluble refrigerante y virutas
Manejo del soluble refrigerante y virutasManejo del soluble refrigerante y virutas View All -
 El Control Haas
El Control HaasEl Control Haas View All
El Control Haas
El Control HaasEl Control Haas View All -
 Opciones para productos
Opciones para productosOpciones para productos View All
Opciones para productos
Opciones para productosOpciones para productos View All -
 Herramientas y sujeción
Herramientas y sujeciónHerramientas y sujeción View All
Herramientas y sujeción
Herramientas y sujeciónHerramientas y sujeción View All -
 Portapiezas
PortapiezasPortapiezas View All
Portapiezas
PortapiezasPortapiezas View All -
 Soluciones de 5 ejes
Soluciones de 5 ejesSoluciones de 5 ejes View All
Soluciones de 5 ejes
Soluciones de 5 ejesSoluciones de 5 ejes View All -
 Automatización
AutomatizaciónAutomatización View All
Automatización
AutomatizaciónAutomatización View All
ENLACES RÁPIDOS Special Series Special SeriesHERRAMIENTAS DE COMPRAS¿QUIERE HABLAR CON ALGUIEN?En su Haas Factory Outlet (HFO) pueden resolver sus dudas y orientarle sobre las mejores opciones.
CONTACT YOUR DISTRIBUTOR > -
-
Main Menu
Descubra la diferencia Haas
-
Servicio técnico
Main Menu
- Videos Main Menu
-
Main Menu
ENLACES RÁPIDOS Special Series Special SeriesHERRAMIENTAS DE COMPRAS¿QUIERE HABLAR CON ALGUIEN?
En su Haas Factory Outlet (HFO) pueden resolver sus dudas y orientarle sobre las mejores opciones.
CONTACT YOUR DISTRIBUTOR >